Random walk hypothesis
The random walk hypothesis is a financial theory stating that stock market prices evolve according to a random walk and thus the prices of the stock market cannot be predicted. It is consistent with the efficient-market hypothesis.
The concept can be traced to French broker Jules Regnault who published a book in 1863, and then to French mathematician Louis Bachelier whose Ph.D. dissertation titled "The Theory of Speculation" (1900) included some remarkable insights and commentary. Same ideas were later developed by MIT Sloan School of Management professor Paul Cootner in his 1964 book The Random Character of Stock Market Prices.[1] The term was popularized by the 1973 book, A Random Walk Down Wall Street, by Burton Malkiel, a Professor of Economics at Princeton University,[2] and was used earlier in Eugene Fama's 1965 article "Random Walks In Stock Market Prices",[3] which was a less technical version of his Ph.D. thesis. The theory that stock prices move randomly was earlier proposed by Maurice Kendall in his 1953 paper, The Analytics of Economic Time Series, Part 1: Prices.[4]
Contents |
Testing the hypothesis
Burton G. Malkiel, an economist professor at Princeton University and writer of A Random Walk Down Wall Street, performed a test where his students were given a hypothetical stock that was initially worth fifty dollars. The closing stock price for each day was determined by a coin flip. If the result was heads, the price would close a half point higher, but if the result was tails, it would close a half point lower. Thus, each time, the price had a fifty-fifty chance of closing higher or lower than the previous day. Cycles or trends were determined from the tests. Malkiel then took the results in a chart and graph form to a chartist, a person who “seeks to predict future movements by seeking to interpret past patterns on the assumption that ‘history tends to repeat itself’”.[5] The chartist told Malkiel that they needed to immediately buy the stock. When Malkiel told him it was based purely on flipping a coin, the chartist was very unhappy. Malkiel argued that this indicates that the market and stocks could be just as random as flipping a coin.
The random walk hypothesis was also applied to NBA basketball. Psychologists made a detailed study of every shot the Philadelphia 76ers made over one and a half seasons of basketball. The psychologists found no positive correlation between the previous shots and the outcomes of the shots afterwards. Economists and believers in the random walk hypothesis apply this to the stock market. The actual lack of correlation of past and present can be easily seen. If a stock goes up one day, no stock market participant can accurately predict that it will rise again the next. Just as a basketball player with the “hot hand” can miss the next shot, the stock that seems to be on the rise can fall at any time, making it completely random.
A non-random walk hypothesis
There are other economists, professors, and investors who believe that the market is predictable to some degree. These people believe that prices may move in trends and that the study of past prices can be used to forecast future price direction. There have been some economic studies that support this view, and a book has been written by two professors of economics that tries to prove the random walk hypothesis wrong.[6]
Martin Weber, a leading researcher in behavioral finance, has performed many tests and studies on finding trends in the stock market. In one of his key studies, he observed the stock market for ten years. Throughout that period, he looked at the market prices for noticeable trends and found that stocks with high price increases in the first five years tended to become under-performers in the following five years. Weber and other believers in the non-random walk hypothesis cite this as a key contributor and contradictor to the random walk hypothesis.[7]
Another test that Weber ran that contradicts the random walk hypothesis, was finding stocks that have had an upward revision for earnings outperform other stocks in the forthcoming six months. With this knowledge, investors can have an edge in predicting what stocks to pull out of the market and which stocks — the stocks with the upward revision — to leave in. Martin Weber’s studies detract from the random walk hypothesis, because according to Weber, there are trends and other tips to predicting the stock market.
Professors Andrew W. Lo and Archie Craig MacKinlay, professors of Finance at the MIT Sloan School of Management and the University of Pennsylvania, respectively, have also tried to prove the random walk theory wrong. They wrote the book A Non-Random Walk Down Wall Street, which goes through a number of tests and studies that try to prove there are trends in the stock market and that they are somewhat predictable.
They prove it with what is called the simple volatility-based specification test, which is an equation that states:
where
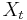 is the price of the stock at time t
is the price of the stock at time t
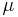 is an arbitrary drift parameter
is an arbitrary drift parameter
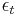 is a random disturbance term.
is a random disturbance term.
With this equation, they have been able to put in stock prices over the last number of years, and figure out the trends that have unfolded.[8] They have found small incremental changes in the stocks throughout the years. Through these changes, Lo and MacKinlay believe that the stock market is predictable, thus contradicting the random walk hypothesis. Lo and MacKinlay have authored a paper, the Adaptive Market Hypothesis, which puts forth another way of looking at predictability of price changes.
See also
References
- ^ Cootner, Paul H. (1964). The random character of stock market prices. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262030090. http://books.google.com/?id=7XGvQgAACAAJ.
- ^ Malkiel, Burton G. (1973). A Random Walk Down Wall Street (6th ed.). W.W. Norton & Company, Inc.. ISBN 0393062457.
- ^ Fama, Eugene F. (September/October 1965). "Random Walks In Stock Market Prices". Financial Analysts Journal 21 (5): 55–59. doi:10.2469/faj.v21.n5.55. http://www.cfapubs.org/toc/faj/1965/21/5. Retrieved 2008-03-21.
- ^ Kendall, M. G.; Bradford Hill, A (1953). "The Analysis of Economic Time-Series-Part I: Prices". Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. A (General) (Blackwell Publishing) 116 (1): 11–34. JSTOR 2980947.
- ^ Keane, Simon M. (1983). Stock Market Efficiency. Philip Allan Limited. ISBN 0860036197.
- ^ Lo, Andrew (1999). A Non-Random Walk Down Wall Street. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691057745.
- ^ Fromlet, Hubert (July 2001). "Behavioral Finance-Theory and Practical Application". Business Economics: 63.
- ^ Lo, Andrew W.; Mackinlay, Archie Craig (2002). A Non-Random Walk Down Wall Street (5th ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 4–47. ISBN 0691092567.